
Fabry-Perot Interferometer
Physikfan, Fri Feb 10 2017, 01:20PMIn order to arouse more interest in my article "Lasermodes of a Green Laser Pointer", I try to get you closer to the Fabry-Perot interferometer.
A Fabry-Pérot interferometer can consist of a transparent plate with two reflective surfaces or two parallel highly reflective mirrors, with a flatness up to Lambda/200 (equivalent to 25 angstroms), such mirrors can cost up to 10,000 $.
The parallelism can be driven so far (for multipass systems) that the deviation over a diameter of 5 cm is less than 5 Angstroms, length of 5 H atoms in a row!
The figure shows an FP schematically with an extended light source:
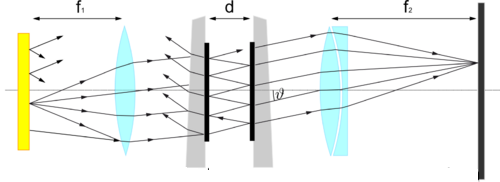
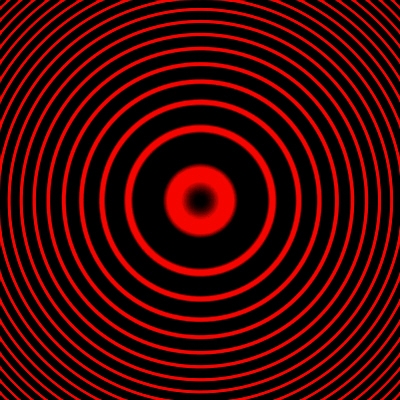
FPs at planar light sources exhibit interference patterns in the form of concentric rings:
A commercial Fabry-Perot, such devices can cost up to 100,000 $:

The transmission spectrum as a function of the wavelength shows peaks of great transmission corresponding to the resonances of the cavity, application as laser resonator.
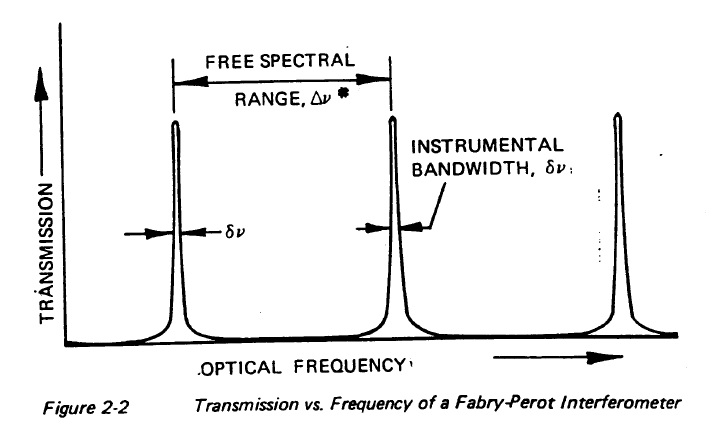
In order to get from one particular order to the next, a mirror must be moved by lambda/2, which is about 250 nm.
The mechanical movement of the mirrors (scanning) is carried out by means of piezoelectrics, which are controlled by triangular voltages of a corresponding height (about 100 V), the fine adjustment of the parallelism also takes place via separate piezoelements.
High-resolution optical spectrum analyzers use confocal Fabry-Pérot interferometers to determine the wavelength of the light with high accuracy.
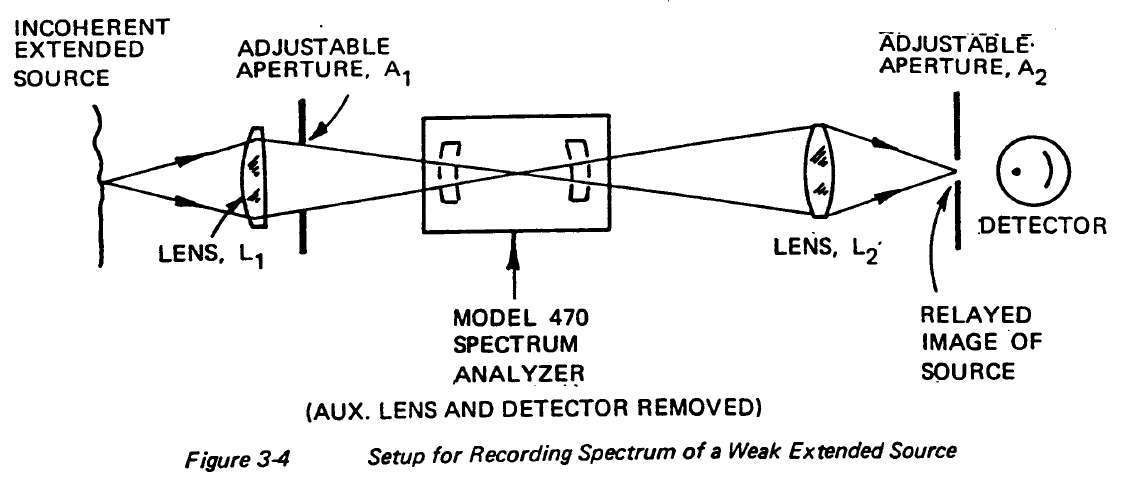
One importanr application:
By inserting a FP etalon within the laser cavity, a laser can be switched from the multimode to single-mode operation.
Further reading:


Print this page